The Challenges of M270 Waste Management for Environmental Cleanup
The Challenges of M270 Waste Management for Environmental Cleanup
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Therapy Technologies and Conveniences
The occurrence of PFAS contamination in water sources demands a thorough understanding of offered treatment innovations. Each technology not only targets particular PFAS substances but additionally plays a critical function in enhancing total water top quality and securing ecological stability.
Comprehending PFAS Contamination
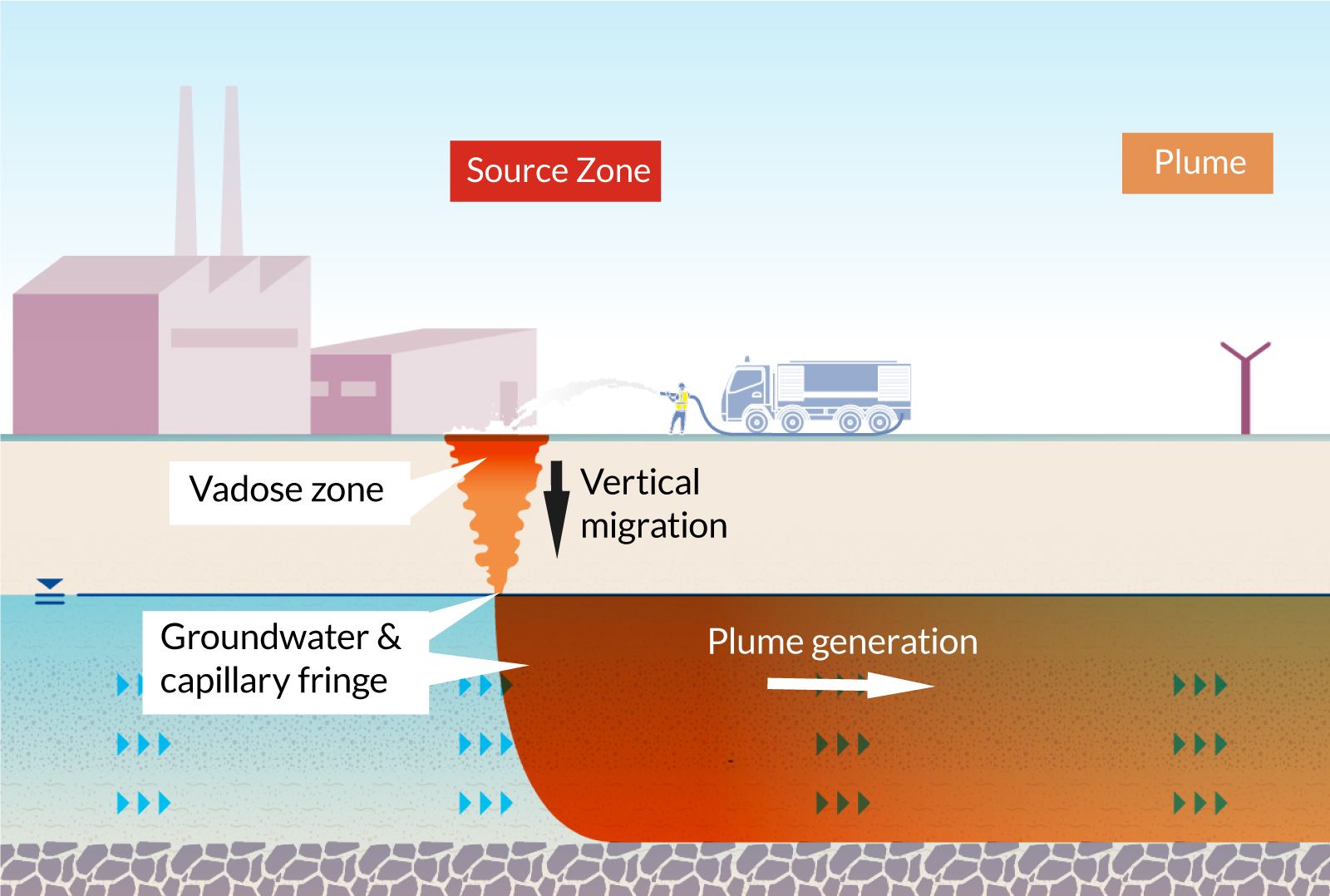
Comprehending PFAS contamination is essential for addressing its pervasive effect on environmental and human health and wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a team of artificial chemicals extensively utilized in numerous commercial and customer items as a result of their water- and grease-resistant properties. Generally located in firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, and water-repellent textiles, PFAS have gotten in the atmosphere through manufacturing procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from landfills
As soon as launched, these materials continue the setting, leading to extensive contamination of dirt and water resources. Their special chemical structure, identified by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, makes them resistant to degradation, leading to a sensation recognized as "forever chemicals." PFAS can build up in the human body and the food chain, possibly causing negative wellness results, including immune system disruption, developmental concerns, and an enhanced threat of specific cancers.
Regulatory companies and health and wellness companies are significantly recognizing the significance of PFAS contamination, triggering initiatives to check, evaluate, and reduce its results. Recognizing the pathways of PFAS contamination is necessary for informing public law and establishing reliable methods to secure both environmental and human health.
Review of Therapy Technologies
Various therapy innovations have been developed to deal with the challenges postured by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These innovations can be broadly identified into a number of groups, each with its unique systems and efficiency in eliminating PFAS substances.
One famous strategy is ion exchange, which utilizes material materials to capture and remove PFAS from polluted water. One more innovation, progressed oxidation procedures (AOPs), employs solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to damage down PFAS into less hazardous compounds.
Turned On Carbon Filtering
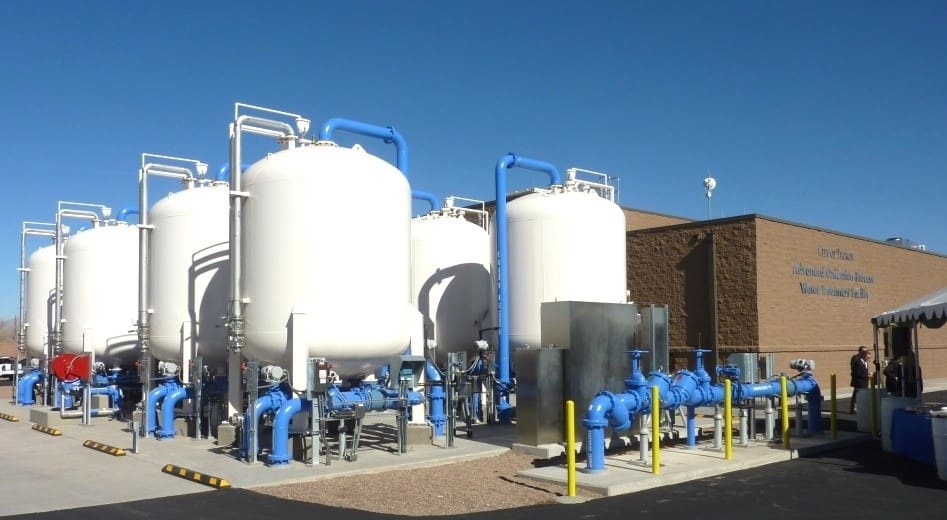
Activated carbon purification is a widely utilized approach for the elimination of PFAS from infected water, understood for its capacity to adsorb a broad series of organic compounds. This innovation utilizes triggered carbon, an extremely porous material with a comprehensive area, which facilitates the binding of PFAS particles via physical adsorption. The efficiency of turned on carbon in getting rid of PFAS is affected by numerous aspects, consisting of the kind of carbon used, the contact time, and the focus of PFAS in the water.
One of the benefits of turned on carbon purification is its versatility; it can be carried out in various configurations, such as granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems or powdered activated carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) systems. GAC systems are generally used in larger-scale applications, while political action committee can be used in smaller or short-term arrangements. In addition, the innovation is reasonably easy to operate and maintain, making it accessible for many water treatment facilities.

Ion Exchange Systems
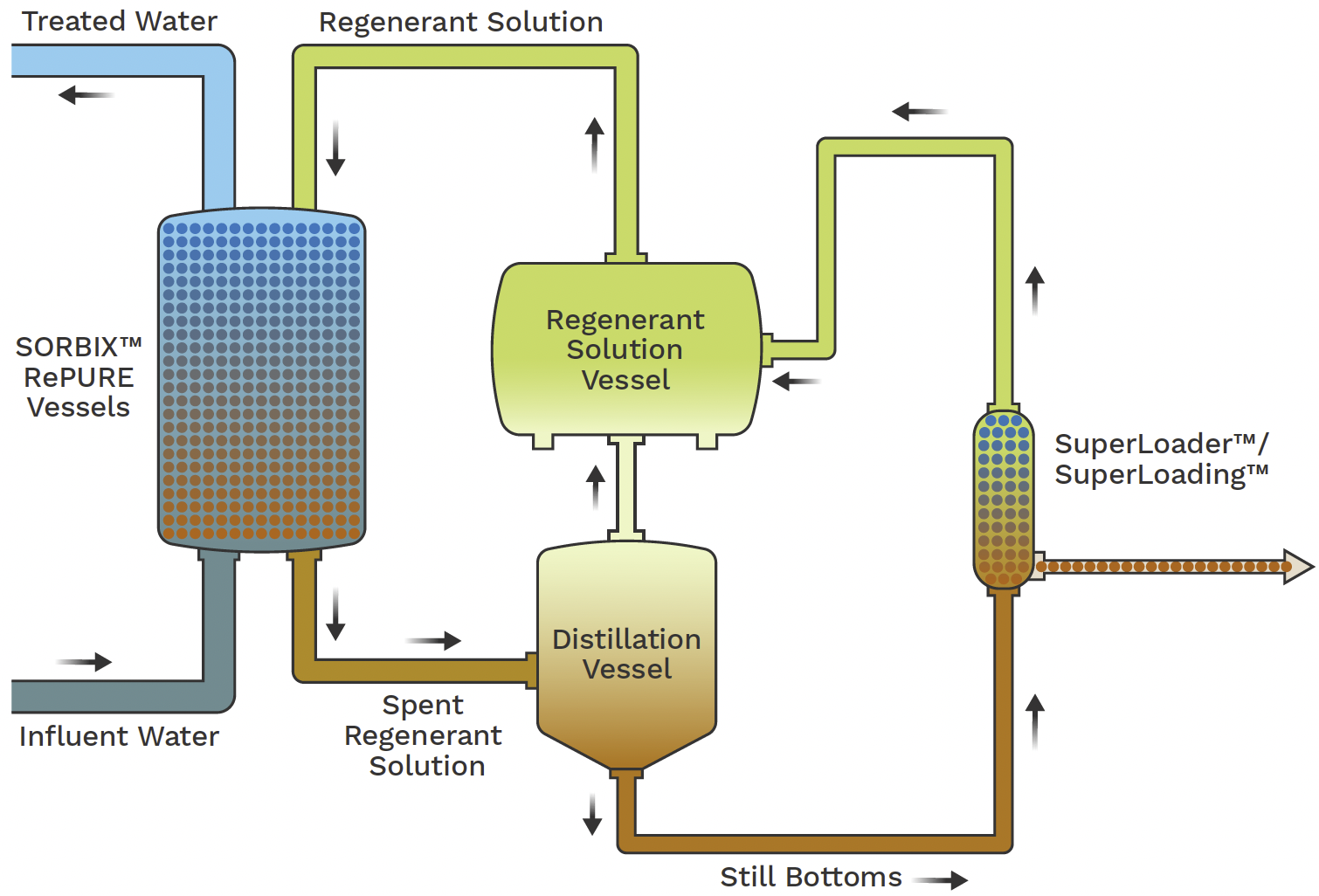
Ion exchange systems stand for an additional efficient approach for the removal of PFAS from infected water, matching techniques like activated carbon filtration. These systems operate on the principle of exchanging ions in the water with ions hung on a resin product. Ion exchange materials can be particularly formulated to try this out target the adversely billed PFAS substances, properly recording them and allowing cleaner water to go through.
One of the key benefits of ion exchange systems is their ability to get rid of a wide variety of PFAS, including both long-chain and short-chain variations. This convenience makes them ideal for numerous applications, ranging from municipal water therapy to commercial processes. Additionally, ion exchange systems can commonly achieve reduced discovery limits for PFAS compared to a few other treatment methods, thus improving water top quality.
Nonetheless, it is important to monitor and handle the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decrease in time due to saturation. Correct maintenance and replacement of the resin are critical for sustaining the system's efficiency. Generally, ion exchange systems supply a reputable and effective remedy for PFAS elimination, adding dramatically to risk-free alcohol consumption water criteria and ecological defense.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) make use of powerful oxidants to effectively deteriorate PFAS substances in infected water. These ingenious therapy approaches produce extremely reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down complicated PFAS particles into less damaging byproducts. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs usually utilize mixes of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, enhancing the oxidation potential and improving destruction effectiveness
The primary advantage of AOPs lies in their capability to target a wide series of PFAS compounds, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variants. This flexibility is essential, as PFAS contamination usually involves blends of different compounds with varying chemical frameworks. Moreover, AOPs can be incorporated into existing water treatment systems, making them a functional option for many districts and markets.
However, the application of AOPs can be resource-intensive, needing cautious factor to consider of operational expenses and power usage. Furthermore, while AOPs work in breaking down PFAS, they might not entirely eliminate all by-products, necessitating additional treatment actions - sites m270 pfas treatment. Generally, AOPs represent an appealing opportunity for dealing with PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water sources and improved public wellness security
Conclusion
Finally, addressing PFAS contamination needs an extensive understanding of readily available treatment innovations. Turned on carbon filtering, ion exchange systems, and advanced oxidation processes each present unique benefits for her response properly removing these unsafe compounds from water resources. By picking the suitable innovation, communities can enhance water quality, protect public wellness, and alleviate the ecological threats connected with PFAS exposure. Continued research and application of these methods are necessary for effective monitoring of PFAS contamination in influenced areas.
Report this page